Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
for the Three Years in the Period Ended June 30, 1999
1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT
ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The accounting policies of Home Federal Bancorp (the "Company")
conform to generally accepted accounting principles and prevailing
practices within the banking and thrift industry. A summary of the
more significant accounting policies follows:
Basis of Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the
Company and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Home Federal Savings
Bank (the "Bank") and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All significant
intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
Description of Business
The Company is a unitary savings and loan holding company. The
Bank provides financial services to south-central Indiana through
its main office in Seymour and 15 other full service branches.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally
accepted accounting principles requires management to make
estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the
financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could
differ from those estimates. Estimates most susceptible to change
in the near term include the allowance for loan losses, mortgage
servicing rights and the fair value of securities.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
All highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three
months or less are considered to be cash equivalents.
Securities
Securities are required to be classified as held to maturity, available
for sale or trading. Debt securities that the Company has the positive
intent and ability to hold to maturity are classified as held to maturity.
Debt and equity securities not classified as either held to maturity
or trading securities are classified as available for sale. Only those
securities classified as held to maturity are reported at amortized
cost, with those available for sale and trading reported at fair value
with unrealized gains and losses included in shareholders' equity or
income, respectively. Premiums and discounts are amortized over
the contractual lives of the related securities using the level yield
method. Gain or loss on sale of securities is based on the specific
identification method.
Loans Held for Sale
Loans held for sale consist of fixed rate mortgage loans conforming
to established guidelines and held for sale to the secondary market.
Mortgage loans held for sale are carried at the lower of cost or market
value determined on an aggregate basis. Gains and losses on the sale
of these mortgage loans are included in other income.
Mortgage Banking Activities
Accounting standards require that the Company recognize as separate
assets, rights to service mortgage loans that have been acquired
through either the purchase or origination of a loan. An entity that
sells or securitizes those loans with servicing rights retained should
allocate the total cost of the mortgage loans to the MSRs and the loans
based on their relative fair values. These costs are initially capitalized
and subsequently amortized in proportion to, and over the period of,
estimated net loan servicing income.
Additionally, MSRs are reported on the Consolidated Balance
Sheets at the lower of cost or fair value. The Company is required
to assess its capitalized MSRs for impairment based upon the fair
value of the rights. MSRs are stratified based upon one or more of
the predominant risk characteristics of the underlying loans.
Impairment is recognized through a valuation allowance for each
impaired stratum.
Loans
Interest on real estate, commercial and installment loans is accrued
over the term of the loans on a level yield basis. The recognition of
interest income is discontinued when, in management's judgment,
the interest will not be collectible in the normal course of business.
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards Nos. 114 and 118
("SFAS 114 and 118"),"Accounting by Creditors for Impairment of a
Loan and Income Recognition and Disclosures," require that impaired
loans be measured based on the present value of expected future cash
flows discounted at the loan's effective interest rate or the fair value
of the underlying collateral, and specifies alternative methods for
recognizing interest income on loans that are impaired or for which
there are credit concerns. For purposes of applying these standards,
impaired loans have been identified as all nonaccrual loans that have
not been collectively evaluated for impairment.
Loan Origination Fees
Nonrefundable origination fees, net of certain direct origination costs,
are deferred and recognized as a yield adjustment over the life of the
underlying loan. Any unamortized fees on loans sold are credited to
gain on sale of loans at the time of sale.
Unearned Discounts
Unearned discounts on mobile home loans are amortized over the
terms of the loans. Amortization is computed by methods which
approximate the interest method.
Uncollected Interest
An allowance for the loss of uncollected interest is provided on loans
which are more than 90 days past due. The allowance is established
by a charge to interest income equal to all interest previously accrued,
and income is subsequently recognized only to the extent that cash
payments are received until, in management's judgment, the
borrower's ability to make periodic interest and principal payments
returns to normal, in which case the loan is returned to accrual status.
Provision for Losses
A provision for estimated losses on loans and real estate owned is
charged to operations based upon management's evaluation of the
potential losses. Such an evaluation, which includes a review of all
loans for which full collectibility may not be reasonably assured,
considers, among other matters, the estimated net realizable value
of the underlying collateral, as applicable, economic conditions,
historical loan loss experience and other factors that are particularly
susceptible to changes that could result in a material adjustment
in the near term. While management endeavors to use the best
information available in making its evaluations, future allowance
adjustments may be necessary if economic conditions change
substantially from the assumptions used in making the evaluations.
Real Estate Owned
Real estate owned represents real estate acquired through foreclosure
or deed in lieu of foreclosure and is recorded at the lower of fair value
and carrying amount. When property is acquired, it is recorded at net
realizable value at the date of acquisition, with any resulting write-down
charged against the allowance for loan losses. Any subsequent
deterioration of the property is charged directly to real estate owned
expense. Costs relating to the development and improvement of real
estate owned are capitalized, whereas costs relating to holding and
maintaining the property are charged to expense.
Premises and Equipment
Premises and equipment are carried at cost less accumulated
depreciation. Depreciation is computed on the straight-line method
over estimated useful lives that range from three to thirty-two years.
Derivatives
The Company has only limited involvement with derivative financial
instruments and does not use them for trading purposes. The
Company has entered into interest rate swap agreements as a
means of managing its interest rate exposure on certain fixed rate
commercial loans. The interest rate swaps are accounted for under
the accrual method. Under this method, the differential to be paid or
received on the interest rate swap agreements is recognized over the
life of the agreement in interest income. Changes in fair value of
interest rate swaps accounted for under the accrual method are not
reflected in the accompanying financial statements. Realized gains
and losses on terminated interest rate swaps are deferred as an
adjustment to the carrying amount of the designated instruments
and amortized over the remaining original life of the agreements.
If the designated instruments are disposed of, the fair value of the
interest rate swap or unamortized deferred gains or losses are
included in the determination of the gain or loss on the disposition
of such instruments. To qualify for such accounting, the interest rate
swaps are designated to specific commercial loans and alter the loan's
interest rate characteristics. The notional amount of the Company's
two outstanding interest rate swap agreements totaled approximately
$5.6 million as of June 30, 1999, and mature in 2008 and 2009,
respectively. The Company did not have any interest rate swap
agreements outstanding at June 30, 1998.
Goodwill
The excess of cost over the fair value of assets acquired in connection
with the purchase of another savings institution is being amortized
using the straight line method over 25 years. Amortization expense
for fiscal years 1999, 1998 and 1997, was $101,000, $101,000 and
$100,000, respectively. Management reviews intangible assets for
possible impairment if there is a significant event that detrimentally
affects operations. Impairment is measured using estimates of the
future earnings potential of the entity or assets acquired.
Income Taxes
The Company and its wholly-owned subsidiary file consolidated
income tax returns. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities reflect
the impact of temporary differences between amounts of assets and
liabilities for financial reporting purposes and basis of such assets
and liabilities as measured by tax laws and regulations.
Earnings per Common Share
Earnings per share of common stock are based on the weighted
average number of basic shares and dilutive shares outstanding
during the year. All per share information has been restated to reflect
the Company's three for two stock split in November 1997.
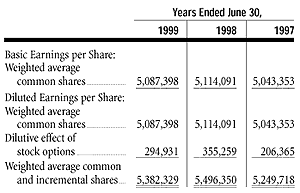 The Company adopted SFAS No. 128,"Earnings per Share,"
for fiscal year 1998 with all prior period earnings per share data
restated. This statement established new accounting standards for the
calculation of basic earnings per share as well as diluted earnings per
share. The adoption of the statement did not have a material effect on
the Company's calculation of earnings per share. The following is a
reconciliation of the weighted average common shares for the basic
and diluted earnings per share computations:
The Company adopted SFAS No. 128,"Earnings per Share,"
for fiscal year 1998 with all prior period earnings per share data
restated. This statement established new accounting standards for the
calculation of basic earnings per share as well as diluted earnings per
share. The adoption of the statement did not have a material effect on
the Company's calculation of earnings per share. The following is a
reconciliation of the weighted average common shares for the basic
and diluted earnings per share computations:
Comprehensive Income
The Company adopted Statement of Financial Accounting Standards
No. 130 ("SFAS 130"),"Comprehensive Income," as of July 1, 1998.
Accounting principles generally require that recognized revenue,
expenses, gains and losses be included in net income, although certain
changes in assets and liabilities, such as unrealized gains and losses
on available-for-sale securities, are reported as a separate component
of the equity section of the balance sheet. Such items, along with net
income, are components of comprehensive income. The adoption of
SFAS 130 had no effect on the Company's net income or shareholders'
equity. All prior year financial statements have been reclassified for
comparative purposes.
The following is a summary of the Company's comprehensive
income for fiscal years 1999, 1998 and 1997 under SFAS 130:
(dollars in thousands)

Segments
Effective July 1, 1998, the Company adopted Statement of Financial
Accounting Standards No. 131 ("SFAS 131"),"Disclosures about
Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information." SFAS 131
redefines how operating segments are determined and requires
disclosure of certain financial and descriptive information about
a company's operating segments. In accordance with SFAS 131,
management has concluded that the Company is comprised of a
single operating segment, community banking activities, and has
disclosed all required information relating to its one operating
segment. Management considers parent company activity to represent
an overhead function rather than an operating segment. The
Company does not have a single external customer from which it
derives 10 percent or more of its revenue and which operates in one
geographical area.
Changes in Presentation
Certain amounts and items appearing in the fiscal 1998 and 1997
financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the fiscal
1999 presentation.
New Accounting Pronouncements
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 133 ("SFAS 133"),
"Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities," was
issued in June 1998 and amended by Statement of Financial Standard
No. 137 ("SFAS 137"),"Accounting for Derivative Instruments and
Hedging Activities-Deferral of the Effective Date of SFAS 133." SFAS
133, as amended by SFAS 137, is effective for all fiscal quarters of all
fiscal years beginning after June 15, 2000. This statement establishes
accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments and
for hedging activities. It requires that an entity recognize all
derivatives as either assets or liabilities in the statement of financial
condition and measure those instruments at fair value. If certain
conditions are met, a derivative may be specifically designated as a
fair value hedge, a cash flow hedge, or a hedge of foreign currency
exposure. The accounting for changes in the fair value of a derivative
(that is, gains and losses) depends on the intended use of the
derivative and the resulting designation. Management has not yet
quantified the effect of this new standard on the consolidated
financial statements.
Previous | Return to Table of Contents | Next
|
 The Company adopted SFAS No. 128,"Earnings per Share,"
for fiscal year 1998 with all prior period earnings per share data
restated. This statement established new accounting standards for the
calculation of basic earnings per share as well as diluted earnings per
share. The adoption of the statement did not have a material effect on
the Company's calculation of earnings per share. The following is a
reconciliation of the weighted average common shares for the basic
and diluted earnings per share computations:
The Company adopted SFAS No. 128,"Earnings per Share,"
for fiscal year 1998 with all prior period earnings per share data
restated. This statement established new accounting standards for the
calculation of basic earnings per share as well as diluted earnings per
share. The adoption of the statement did not have a material effect on
the Company's calculation of earnings per share. The following is a
reconciliation of the weighted average common shares for the basic
and diluted earnings per share computations:
