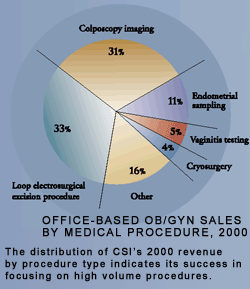
CSI's
group of products for the practitioner's office addresses high volume clinical
conditions:
Abnormal Pap Smears: When a Pap test result
is abnormal, the physician often repeats it or performs a colposcopic examination-a
visual inspection of the cervix and surrounding tissues—and samples suspicious
tissue. Depending on the result, the physician may recommend a follow-up
Pap and colposcopic examination or a Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure
(LEEP) to biopsy tissue, remove it or both.
 CSI
offers a complete product line to support the evaluation of abnormal Pap
smears: vaginal specula, the Cervex - Brush for specimen collection,
colposcopes with supporting instrumentation and a full LEEP product line. CSI
offers a complete product line to support the evaluation of abnormal Pap
smears: vaginal specula, the Cervex - Brush for specimen collection,
colposcopes with supporting instrumentation and a full LEEP product line.
CSI entered the colposcopy market with its 1990 acquisition of Frigitronics
and later introduced the first overhead colposcopy unit specifically designed
for LEEP.
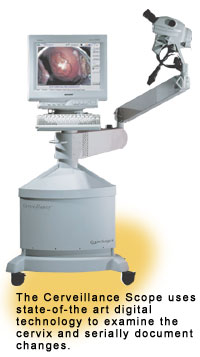
In 1998, CSI introduced, the Cerveillance Scope, which uses digital
technology to visualize and document cervical lesions. This is the first
device to combine digital imaging technology and proprietary software
in a fully integrated compact instrument. CSI became a world leader in
colposcopy with its 2000 acquisition of Leisegang Medical, a leading colposcopy
manufacturer.
In 1991, CSI introduced the LEEP procedure to the United States market
and followed with a complete line of products to surround it. These include
the LEEP System 1000 electrosurgical generator, the CooperSurgical
Smoke Evacuation System 6080, and the non-conductive, autoclavable
instrumentation and ancillary disposable products used in each case. It
also includes the Prima Series speculum that resists staining and
surface degradation, and disposable products such as sterile single use
LEEP electrodes and LEEP RediKit.
Menopause: Menopause is the permanent
cessation of menstruation after loss of ovarian function. As the female
population has aged, visits related to menopause have grown to over 10
million per year>8. The United States Census
Bureau projects a 30 percent increase in women in this age group over
the next ten years.
|
Office Based Gynecology
Procedures
|
|
Reason for Visit
|
Annual Office
Visits, 1999 (000's)
|
Rank in Annual
Visits to Ob/Gyns
|
Product Categories Used
|
|
|
|
Gynecological examinations
|
13,658
|
|
Third
|
• Vaginal specula
• Pap smear
|
|
Menopause
|
10,247
|
|
Fourth
|
• Endometrial sampling
|
|
Menstrual disorders
|
5,230
|
|
Fifth
|
• Endometrial sampling
• Hysteroscopy
|
|
Abnormal Pap smear
|
4,840
|
|
Sixth
|
• LEEP products
• Colposcopes
• Pap smear
|
|
Vaginitis
|
4,398
|
|
Seventh
|
• Vaginitis testing
|
|
Female genital symptoms
|
1,570
|
|
Tenth
|
• Cryosurgery
• Electrosurgery
|

Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is recommended for the primary symptoms
of menopause — hot flashes and vaginal atrophy - and to reduce the long-term
effects of estrogen deficiency: cardiovascular disease, weakening of the
pelvic support structures and osteoporosis. Before starting HRT, physicians
often sample cells from the endometrium, particularly when bleeding is
irregular or heavy. With some therapeutic regimens, physicians test annually
to monitor the thickening of the uterine lining, which occurs in up to
30 percent of women receiving estrogens alone as their HRT8
[8Menopause. In: Visscher CH, ed. Précis V, An Update
in Obstetrics and Gynecology, American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
1994; 404. ]
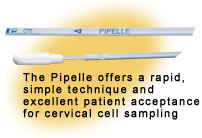
Endometrial cell sampling helps evaluate abnormal uterine bleeding in
women at risk for endometrial polyps or abnormal cellular growth. Clinicians
regard CSI's Pipelle, a disposable aspiration device, as the premier product
for this procedure.
Menstrual Disorders: Office
visits for menstrual disorders have risen significantly in the last five
years. There are three main classes: abnormal uterine bleeding, the absence
of a menstrual cycle, and a painful menstrual cycle. More than 50 percent
of women experience pain associated with their menstrual cycle9. A comprehensive
differential diagnosis of this condition often includes laparoscopy.
Abnormal uterine bleeding is common in women approaching menopause. The
standard diagnostic process involves a physical examination, blood tests,
pelvic ultrasound and endometrial biopsy, where the CSI Pipelle
is used.
Anatomic causes of abnormal uterine bleeding, including benign tumors
that are found in about 50 percent of women over 3510, are identified through laparoscopic
or hysteroscopic examination. Operative hysteroscopy is often performed
to remove benign tumors.
 Hysteroscopy
is performed either in the physician's office or at the hospital. Diagnostic
hysteroscopy provides a direct view of uterine cavity abnormalities before
treatment. The equipment required includes a scope, a light source and
a mechanism to distend the uterus. Operative hysteroscopy is usually performed
in hospitals or at outpatient surgical facilities. Hysteroscopy
is performed either in the physician's office or at the hospital. Diagnostic
hysteroscopy provides a direct view of uterine cavity abnormalities before
treatment. The equipment required includes a scope, a light source and
a mechanism to distend the uterus. Operative hysteroscopy is usually performed
in hospitals or at outpatient surgical facilities.
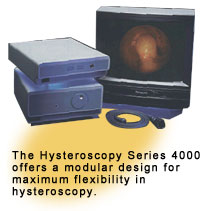
CSI offers an array of diagnostic hysteroscopy products including a fully
integrated system with light source, camera and monitor for office use,
and a variety of hysteroscopes. CSI also markets Hyskon, a solution
used to distend the uterus.
9[Rapkin
A. Pelvic Pain and Dysmenorrhea. In Berek ed., Novak's Gynecology, 12th
Edition. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1996; 408. ]
10[Hillard
P. Benign Diseases of the Female Reproductive Tract: Symptoms and Signs.
In: Berek JS ed., Novak's Gynecology, 12th Edition. Baltimore: Williams
& Wilkins, 1996; 408.]
Vaginitis: The signs of vaginitis are
redness, swelling and discharge caused by an infection or disturbance
in the vaginal ecosystem mainly due to bacterial vaginosis (BV), Candidiasis
(yeast), and Trichomoniasis.
Apart from physical discomfort, the consequences of yeast infections are
relatively benign. BV and Trichomoniasis infections, however, can lead
to serious consequences. BV has been associated with early pregnancy loss,
preterm delivery, premature rupture of membranes, and postpartum endometritis
as well as post surgical infections and pelvic inflammatory disease. Trichomoniasis
is linked to postoperative infection, preterm delivery and premature rupture
of membranes. The differential diagnosis of vaginitis includes evaluation
of the discharge through pH measurement and determina-tion of the presence
or absence of amines.
In 1998, CSI introduced FemExam pH and Amines TestCard,
a point of care diagnostic test used to differentiate these infections.
The card objectively indicates elevated pH and the presence of amines,
two of the four criteria used to diagnose BV. When positive, these two
criteria provide a presumptive diagnosis of BV. During 2000, the American
Medical Association created a specific reimbursement code for amines testing
to supplement the existing code for pH testing. The Health Care Financing
Administration has set a suggested reimbursement rate.
 Female
Genital Symptoms: Most cases of Female Genital Symptoms relate
to the human papilloma virus (HPV), which is the most common sexually
transmitted viral infection in the United States. Manifestations of HPV
include genital warts and precancerous conditions of the cervix and the
vagina. Diagnosis is through colposcopic inspection, and where indicated,
biopsy. There are no known cures. Treatment regimens include keratolytic
agents that promote skin shedding, immunotherapy and surgical procedures
such as cryosurgery, electrocautery (LEEP) and laser therapy. CSI offers
both electrosurgical and cryosurgical equipment for office-based treatment
of differing stages of the infection. Female
Genital Symptoms: Most cases of Female Genital Symptoms relate
to the human papilloma virus (HPV), which is the most common sexually
transmitted viral infection in the United States. Manifestations of HPV
include genital warts and precancerous conditions of the cervix and the
vagina. Diagnosis is through colposcopic inspection, and where indicated,
biopsy. There are no known cures. Treatment regimens include keratolytic
agents that promote skin shedding, immunotherapy and surgical procedures
such as cryosurgery, electrocautery (LEEP) and laser therapy. CSI offers
both electrosurgical and cryosurgical equipment for office-based treatment
of differing stages of the infection.
|

 CSI
offers a complete product line to support the evaluation of abnormal Pap
smears: vaginal specula, the Cervex - Brush for specimen collection,
colposcopes with supporting instrumentation and a full LEEP product line.
CSI
offers a complete product line to support the evaluation of abnormal Pap
smears: vaginal specula, the Cervex - Brush for specimen collection,
colposcopes with supporting instrumentation and a full LEEP product line.