With some 300 catalog items and more than 170 safety-related U.S. patents, BD offers today’s most complete line of advanced protection products. This position of leadership evolved through continuous change over many years, but it was punctuated by two landmark events.
The first occurred near the end of the Company’s sixth decade. Until that time, BD had manufactured and sold reusable glass syringes that were sterilized after each use. That changed when sterile disposables emerged as a better way to reduce the spread of infection among patients. To raise the huge amount of capital needed to reengineer its products and production systems, BD became a publicly-held company in 1962.
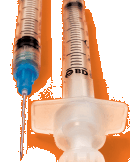
| The BD Integra syringe with
retracting BD PrecisionGlide
needle offers a range of
benefits: safer products for
the healthcare worker, the
flexibility to change needles,
comfort for the patient and
very low medication waste. |
 |
While the transition to disposables addressed the issue of infection spread to patients from unsterile devices, an additional concern emerged–spread of infection to healthcare workers from sharps injuries. The risks stemming from sharps injuries were highlighted in 1987 with the first transmission
of HIV due to an occupational injury. BD–already at work developing safety-engineered products–responded by introducing the BD Safety-Lok syringe the very next year. The Company broadened its line in the early and mid-1990s, including the BD SafetyGlide needle, the first safety-engineered injection device featuring single-handed activation.
By the later 1990s, the stage was set for the second sweeping change: the conversion to safety-engineered sharps products, a commitment entailing hundreds of millions of dollars in new production systems and product redesign. As a result, BD offers a wide range of advanced protection devices for blood collection, infusion therapy and injection, and also offers safety-engineered designs for prefills, critical care, surgery and other lines.
Last year, BD introduced the first of a new generation of safety-engineered injection devices, the BD Integra syringe with retracting BD PrecisionGlide needle. This combination of syringe and needle offers an interchangeable needle–a BD exclusive–that allows clinicians to use different needle sizes for drawing medications and injecting patients. Since research indicates that many clinicians prefer to retract the needle after it is withdrawn, the BD Integra offers them the freedom of choosing that method or activating the safety mechanism while the needle is still inside the patient. Patient comfort is further enhanced with BD PrecisionGlide needles, the world’s sharpest. And, the BD Integra syringe significantly reduces the amount of wasted medication left in the syringe after use by up to 90 percent compared with other retracting designs, resulting in less waste compared with conventional syringes. This savings translates into the ability to obtain an additional dose of medication per vial, reducing costs and stretching medications that may be in short supply.
|



