|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
spent on computer software projects. Costs associated with preliminary stage activities, training, maintenance and all other post-implementation stage activities are expensed as incurred. All costs capitalized in
connection with internal use computer software projects are
amortized on a straight-line basis over a useful life of five years.
Financial Instruments
The company adopted the provisions of Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 133, "Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities" (SFAS No. 133), as amended, effective February 4, 2001, as discussed in the footnote entitled "DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES." This statement requires
that all derivatives be recorded on the balance sheet at fair value
and that changes in fair value be recognized currently in earnings
unless specific hedge accounting criteria is met.
The company enters into forward foreign exchange contracts to minimize the risk associated with currency movement relating to its short-term intercompany loan program with foreign subsidiaries. Gains and losses, which offset the movement in the underlying transactions, are recognized as part of such transactions. Gross deferred unrealized losses on the forward contracts were not material at either February 1, 2003 or at February 2, 2002. The related receivable, payable and deferred gain or loss are included on a net basis in the balance sheet. The company had $205 and $108 of short-term outstanding forward contracts at February 1, 2003 and February 2, 2002, maturing in 2003 and 2002, respectively. These contracts are entered into with counter-parties that have high credit ratings and with which the company has the contractual right to net forward currency settlements.
Stock Options
The company accounts for stock options in accordance with the
provisions of Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 25, "Accounting for Stock Options Issued to Employees" (APB 25).
The company has adopted the disclosure only provisions of SFAS No. 123 "Accounting for Stock Based Compensation" (FAS 123),
issued in 1995.
In accordance with the provisions of SFAS No. 123, the company applies APB Opinion No. 25 and related interpretations in accounting for its stock option plans and, accordingly, does not recognize compensation cost. If the company had elected to recognize compensation cost based on the fair value of the options granted at grant date as prescribed by SFAS No. 123, net earnings and earnings per share would have been reduced to the pro forma amounts indicated in the following table: |
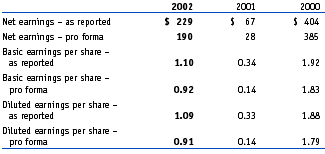
The weighted-average fair value at the date of grant for options granted in 2002, 2001 and 2000 was $6.42, $9.16 and $5.88, respectively. The fair value of each option grant is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. As there were a number of options granted during the years of 2000 through 2002, a range of assumptions are provided below:
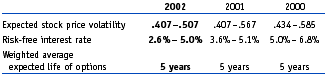
The effects of applying SFAS No. 123 and the results obtained through the use of the Black-Scholes option pricing model are
not necessarily indicative of future values.
RESTRICTED CASH
The company had restricted cash of $60 at February 1, 2003.
Included in this amount is $45 being used as support for a letter
of credit in exchange for reduced letter of credit fees. This letter
of credit partially supports the company's 475 Swiss Franc note, due January 28, 2004. The remaining $15 relates to a pending real estate transaction that is expected to close in 2003.
MERCHANDISE INVENTORIES
Merchandise inventories for the U.S. toy store division are stated at the lower of LIFO (last-in, first-out) cost or market. If inventories
had been valued at the lower of FIFO (first-in, first-out) cost or
market, inventories would show no change at February 1, 2003 or February 2, 2002.
|