|
Diabetes and Obesity
OSI confirmed its commitment to finding medicines that can help people
with diabetes with the April 2005 consolidation of Prosidion into OSI
as a wholly owned subsidiary. This was achieved through the buy-back
of shares from minority shareholders.
OSI has a 14-year history of diabetes research including alliances with
international pharmaceutical companies such as Wyeth and Tanabe Seiyaku
Co., Ltd. Prosidion, established in 2003 as a vehicle to advance and
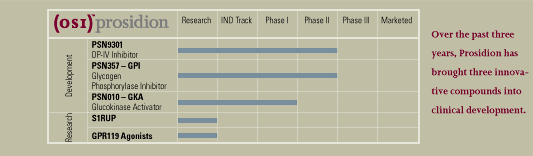
develop OSI’s diabetes and obesity assets, has progressed three
compounds into clinical development. It acquired the Phase II DP-IV inhibitor
PSN9301 and a DP-IV inhibitor patent estate from Probiodrug AG. Through
our Prosidion team, OSI believes it can produce a pipeline of innovative
and competitive diabetic drug candidates.
PSN9301, PSN357 and PSN010 are our three leading diabetes and obesity
candidates. PSN9301, a small molecule DP-IV inhibitor, is currently in
Phase II clinical trials. DP-IV is one of the most important targets
in diabetes drug development today. DP-IV inactivates a natural hormone
produced by the body after meals that helps regulate meal-related increases
in glucose called GLP-1. DP-IV inhibitors help maintain GLP-1 levels.
This area is competitive, but we believe PSN9301, which is designed to
be prandially dosed – taken with meals – could offer advantages
in terms of minimizing potential side effects and providing an optimal
profile for combination with other diabetes drugs such as metformin.
We have also out-licensed our DP-IV medical-use patents to six major
pharmaceutical companies, including Novartis AG and Merck & Co. These
licenses provide us with milestone and royalty payments. With both Novartis
and Merck having recently filed NDAs for their DP-IV inhibitors (Januvia™ from
Merck and Galvus™ from Novartis), we expect both milestone and
royalty payments from these companies if their agents are successfully
registered.
PSN357, a glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor, entered a Phase IIa clinical
trial in late February of 2006. It has demonstrated safety in Phase I
trials and efficacy in reducing blood glucose in animal models. PSN010
is a glucokinase activator which has recently begun clinical trials.
It has a dual effect on the liver and the pancreas, resulting in increased
hepatic glucose uptake in the liver and stimulated insulin secretion
by the pancreas. It, too, has demonstrated efficacy in animal models
and successfully completed pre-clinical toxicological profiling.
Behind these clinical candidates we also have two potential drug candidates
for obesity, a growing health concern related to occurrence of diabetes.
|