



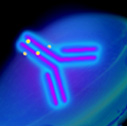


An immunoconjugate anticancer drug
consists of a tumor-targeting monoclonal
antibody – a manufactured protein created
to bind specifically to a target found on
cancer cells – with an attached cell-killing,
or cytotoxic, agent. The antibody component
enables the immunoconjugate to bind
specifically to the cancer cells that have its
target on their surface and the cytotoxic
agent serves to kill the cancer cells.