|
 |
 |
The notional amounts of open forward contracts and options for continuing operations were $505 million at December 31, 2001 and $281 million at December 31, 2000. Amounts related to discontinued operations were $61 million at December 31, 2000. The notional amounts of our foreign exchange contracts do not generally represent amounts exchanged by the parties, and thus, are not a measure of our exposure or of the cash requirements relating to these contracts. The amounts exchanged are calculated by reference to the notional amounts and by other terms of the derivatives, such as exchange rates.
Financial instruments that potentially subject us to concentrations of credit risk are primarily cash equivalents, investments and trade receivables. It is our practice to place our cash equivalents and investments in high-quality securities with various investment institutions. We derive the majority of our revenues from sales and services, including engineering and construction, to the energy industry. Within the energy industry, trade receivables are generated from a broad and diverse group of customers. There are concentrations of receivables in the United States and the United Kingdom. We maintain an allowance for losses based upon the expected collectibility of all trade accounts receivable.
There are no significant concentrations of credit risk with any individual counterparty related to our derivative contracts. We select counterparties based on their profitability, balance sheet and a capacity for timely payment of financial commitments which is unlikely to be adversely affected by foreseeable events.
We have several debt instruments outstanding which have both fixed and variable interest rates. We manage our ratio of fixed to variable-rate debt through the use of different types of debt instruments and derivative instruments.
The estimated fair market value of long-term debt at year-end 2001 was $1.3 billion and in 2000 was $1.1 billion as compared to the carrying amount of $1.5 billion at year-end 2001 and $1.1 billion at year-end 2000. The fair market value of fixed rate long-term debt is based on quoted market prices for those or similar instruments. The carrying amount of variable rate long-term debt approximates fair market value because these instruments reflect market changes to interest rates. See Note 8. The carrying amount of short-term financial instruments, cash and equivalents, receivables, short-term notes payable and accounts payable, as reflected in the consolidated balance sheets approximates fair market value due to the short maturities of these instruments. The currency derivative instruments are carried on the balance sheet at fair value and are based upon third-party quotes. The fair market values of derivative instruments used for fair value hedging and cash flow hedging were immaterial.
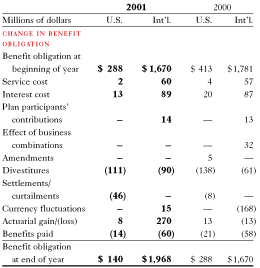
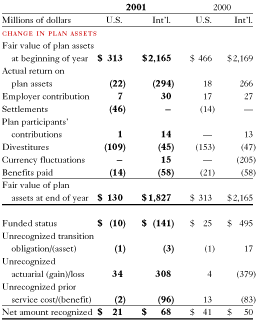
Our company and subsidiaries have various plans which cover a significant number of their employees. These plans include defined contribution plans, which provide retirement contributions in return for services rendered, provide an individual account for each participant and have terms that specify how contributions to the participant’s account are to be determined rather than the amount of pension benefits the participant is to receive. Contributions to these plans are based on pretax income and/or discretionary amounts determined on an annual basis. Our expense for the defined contribution plans for both continuing and discontinued operations totaled $129 million in 2001 compared to $140 million in 2000 and $111 million in 1999. Other retirement plans include defined benefit plans, which define an amount of pension benefit to be provided, usually as a function of age, years of service or compensation. These plans are funded to operate on an actuarially sound basis. Plan assets are primarily invested in cash, short-term investments, real estate, equity and fixed income securities of entities domiciled in the country of the plan’s operation. Plan assets, expenses and obligations for retirement plans in the following tables include both continuing and discontinued operations.
|
|
|