Financial Information
17. VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
Under the applicable accounting guidance for the consolidation of variable interest entities, we analyze our variable interests, including loans, guarantees, and equity investments, to determine if an entity in which we have a variable interest is a variable interest entity. Our analysis includes both quantitative and qualitative reviews. We base our quantitative analysis on the forecasted cash flows of the entity, and our qualitative analysis on our review of the design of the entity, its organizational structure including decision-making ability, and relevant financial agreements. We also use our qualitative analysis to determine if we must consolidate a variable interest entity as its primary beneficiary.
Variable interest entities related to our timeshare note securitizations
Before the spin-off, we periodically securitized, without recourse, through special purpose entities, notes receivable originated by our former Timeshare segment in connection with the sale of timeshare interval and fractional products. These securitizations provided funding for us and transferred the economic risks and substantially all the benefits of the loans to third parties. In a securitization, various classes of debt securities that the special purpose entities issued were generally collateralized by a single tranche of transferred assets, which consisted of timeshare notes receivable. We serviced the notes receivable. With each securitization, we retained a portion of the securities, subordinated tranches, interest-only strips, subordinated interests in accrued interest and fees on the securitized receivables or, in some cases, overcollateralization and cash reserve accounts. As a result of our involvement with these entities in 2011 before the spin-off, we recognized $116 million of interest income, partially offset by $39 million of interest expense to investors and $3 million in debt issuance cost amortization. Similarly for 2010, we recognized $147 million of interest income, partially offset by $51 million of interest expense to investors, and $4 million in debt issuance cost amortization.
We show our cash flows to and from the timeshare notes securitization variable interest entities in the following table for 2011 before the spin-off and for 2010:
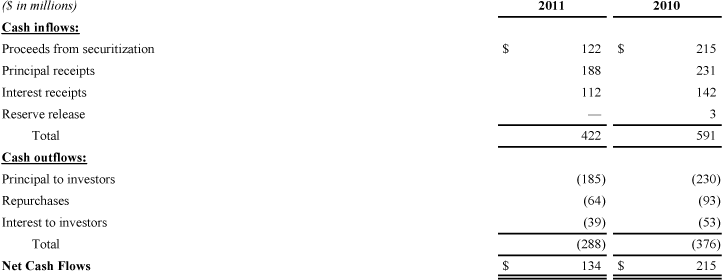
Under the terms of our timeshare note securitizations, we had the right at our option to repurchase defaulted mortgage notes at the outstanding principal balance. The transaction documents typically limited such repurchases to 10 to 20 percent of the transaction’s initial mortgage balance. We voluntarily repurchased $43 million of defaulted notes during 2011 and $68 million during 2010. We also voluntarily repurchased $21 million of other non-defaulted notes during 2011 and $25 million during 2010.
Other variable interest entities
In conjunction with the transaction with CTF that we described more fully in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for 2007 in Footnote No. 8, “Acquisitions and Dispositions,” under the caption “2005 Acquisitions,” we manage hotels on behalf of tenant entities that are 100 percent owned by CTF, which lease the hotels from third-party owners. Due to certain provisions in the management agreements, we account for these contracts as operating leases. At year-end 2012, we managed five hotels on behalf of three tenant entities. The entities have minimal equity and minimal assets, consisting of hotel working capital and furniture, fixtures, and equipment. As part of the 2005 transaction, CTF placed money in a trust account to cover cash flow shortfalls and to meet rent payments. In turn, we released CTF from its guarantees fully for three of these properties and partially for the other two properties. The trust account was fully depleted prior to year-end 2011. The tenant entities are variable interest entities because the holder of the equity investment at risk, CTF, lacks the ability through voting rights to make key decisions about the entities’ activities that have a significant effect on the success of the entities. We do not consolidate the entities because we do not have: (1) the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the entities’ economic performance or (2) the obligation to absorb losses of the entities or the right to receive benefits from the entities that could potentially be significant. We are liable for rent payments for three of the five hotels if there are cash flow shortfalls. Future minimum lease payments through the end of the lease term for these hotels totaled approximately $12 million at year-end 2012. In addition, as of year-end 2012 we are liable for rent payments of up to an aggregate cap of $5 million for the two other hotels if there are cash flow shortfalls. Our maximum exposure to loss is limited to the rent payments and certain other tenant obligations under the lease, for which we are secondarily liable.
