The need to diagnose and treat patients quickly and effectively in hospitals and clinics is matched by the need to deliver those treatments with minimal risks to both patients and healthcare providers. BD offers a comprehensive line of innovative injection and infusion devices that effectively deliver lifesaving therapies and vaccines, while reducing the risk of needlestick injury or other incidents that may spread infection.
Reducing the spread of infection
Needlestick injuries, which expose healthcare workers to such dangerous pathogens as hepatitis C and HIV, are a serious occupational hazard. For two decades, BD has been a pioneer and world leader in developing advanced safety-engineered delivery systems designed to protect healthcare workers and patients from exposures to bloodborne pathogens.
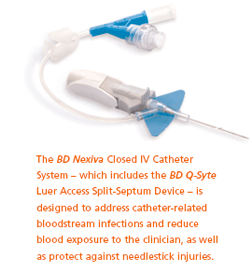
One of BD's innovative solutions is the BD Nexiva Closed IV Catheter System. This simple, all-in-one product is designed to increase first-stick success and reduce blood exposure to clinicians through its innovative blood containment system. This product is often coupled with the BD Q-Syte Luer Access Split-Septum Device, which helps reduce the risk of catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs). Studies indicate that a split-septum needleless access systems have 64 percent to 70 percent lower CRBSI rates than mechanical valves.
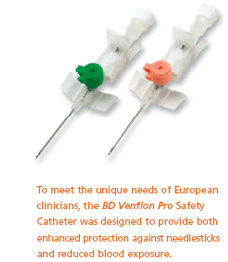
The Company also developed the BD Venflon Pro Safety IV Catheter for the clinical environment in Europe. Its unique features are designed to help protect healthcare workers from needlestick injuries and blood splatter that can occur during the IV cannulation process. Such safety-engineered products are needed in healthcare institutions across Europe, where an estimated 1 million needlesticks occur every year.
Delivering medicines more effectively
In demanding clinical environments, it is critical to minimize the risk of medical errors, preserve the supply of vaccines and medicines, and reduce the time it takes to prepare treatments. When compared with single- and multi-dose vials, prefilled syringes address these concerns for the benefit of both patients and providers.

Getting to Zero: Catheter-related Bloodstream Infections in the ICU Clinicians at Jennie Edmundson Hospital (JEH) in Council Bluffs, Iowa, sought ways to reduce catheterrelated bloodstream infections (CRBSIs) in its 13-bed Intensive Care Unit (ICU). CRBSIs are potentially fatal, especially for critically ill ICU patients, and they can dramatically increase healthcare costs. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services estimate that a vascular catheter-associated infection can increase the cost of a hospital stay by more than $100,000 per patient.
Kari Love, RN, Clinical Quality Specialist in Infection Prevention at JEH, studied the impact of switching to the simple BD Q-Syte Luer Access Split-Septum Devices from complex mechanical valves, which can harbor bacteria that pose a risk to patients receiving intravenous therapy.
For the 10 months prior to the switch, the facility's average infection rate was slightly more than three per month - lower than the national benchmark, but still unacceptable to JEH. Using BD Q-Syte Devices, Love reduced the infection rate to zero throughout the eight-month period studied.
According to Love, "With the increasing prevalence of drug-resistant infections, it is encouraging to find simple ways to reduce risks to patients."
Love and her study team continue to evaluate the impact of using BD Q-Syte Devices in other units, with the ultimate goal of eliminating CRBSIs throughout the hospital.
BD remains at the forefront of injection technology with such products as BD Hypak SCF Glass Prefillable Syringes, a complete drug delivery system that may reduce the risk of medication errors and contamination that can occur during the traditional vial-to-syringe filling process.
BD has developed the novel BD Soluvia Prefillable Microinjection System. While most vaccines are injected into the muscle, this system uses innovative BD micro-delivery technology to deliver vaccines intradermally - within the dermal layer of the skin, which may enable the vaccine to enter the immune system more efficiently.
In clinical trials on more than 7,000 subjects, intradermal delivery of the influenza vaccine provided an improved immune response in the elderly. In other trials, the BD Soluvia System demonstrated that injections to the dermal layer worked effectively regardless of the subject's gender, age, ethnicity and body mass.
Leading the way in global immunizations
BD continues to play a leading role in global immunization efforts. For decades, the Company has collaborated with governments, health agencies and non-governmental organizations to achieve cost-effective and safe immunization of children in developing countries. In fact, more than 6 billion safe immunizations have been administered worldwide using the Company's low-cost, auto-disable devices, such as BD SoloShot Syringes.
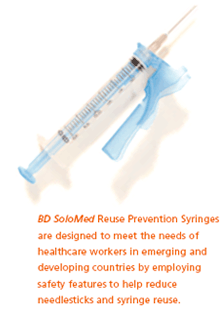
For curative or therapeutic injection applications, BD SoloMed Syringes were recently introduced to reduce the incidence of intentional syringe reuse and provide protection against needlesticks in emerging and developing countries. This low-cost injection device employs a needle safety shield to help protect healthcare workers. It also features a plunger that is easily disabled after one injection, preventing the syringe from being reused.
The BD Uniject Prefillable, Auto-disable Injection System is designed to prevent reuse and eliminate the need for filling syringes from vials. Its innovative design is particularly suited for administering injections in remote settings in the developing world. Through a Program for Appropriate Technology in Health (PATH) project funded by USAID, the BD Uniject System has been approved in Latin America for use with oxytocin, a drug used to prevent post-partum hemorrhage. It also has been utilized for tetanus toxoid vaccinations in Africa.